03. Hello, Tensor World!
Hello, Tensor World!
让我们来分析一下你刚才运行的 Hello World 的代码。代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf
# Create TensorFlow object called hello_constant
hello_constant = tf.constant('Hello World!')
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Run the tf.constant operation in the session
output = sess.run(hello_constant)
print(output)Tensor
在 TensorFlow 中,数据不是以整数、浮点数或者字符串形式存储的。这些值被封装在一个叫做 tensor 的对象中。在 hello_constant = tf.constant('Hello World!') 代码中,hello_constant 是一个 0 维度的字符串 tensor,tensor 还有很多不同大小:
# A is a 0-dimensional int32 tensor
A = tf.constant(1234)
# B is a 1-dimensional int32 tensor
B = tf.constant([123,456,789])
# C is a 2-dimensional int32 tensor
C = tf.constant([ [123,456,789], [222,333,444] ])tf.constant() 是你在本课中即将使用的多个 TensorFlow 运算之一。tf.constant() 返回的 tensor 是一个常量 tensor,因为这个 tensor 的值不会变。
Session
TensorFlow 的 api 构建在 computational graph 的概念上,它是一种对数学运算过程进行可视化的方法(在 MiniFlow 这节课中学过)。让我们把你刚才运行的 TensorFlow 代码变成一个图:
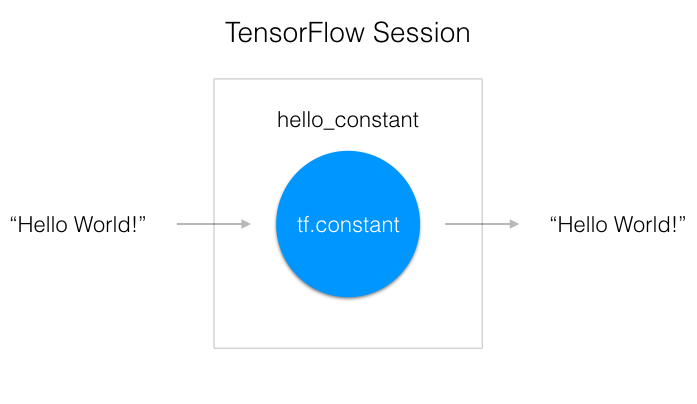
如上图所示,一个 "TensorFlow Session" 是用来运行图的环境。这个 session 负责分配 GPU(s) 和/或 CPU(s),包括远程计算机的运算。让我们看看如何使用它:
with tf.Session() as sess:
output = sess.run(hello_constant)代码已经从之前的一行中创建了 tensor hello_constant。接下来是在 session 里对 tensor 求值。
这段代码用 tf.Session 创建了一个 sess 的 session 实例。然后 sess.run() 函数对 tensor 求值,并返回结果。